Today’s modern world implies that business companies are keen on finding ways to make their work faster and more effective. Enterprise software development is central to the fulfilment of these objectives as it enables the right solutions to be implemented for particular business requirements. This blog focuses on the subject of enterprise software development and its effects on business development and performance. We will later learn about the different categories of enterprise software, what to consider when selecting, and the value the software delivers to organisations.
The Role of Enterprise Software in Modern Businesses
Enterprise software is the core of numerous modern firms and provides solutions aimed at handling business processes efficiently. These applications run in addition to off-the-shelf business software solutions that suit the particular needs of the industry and can easily interface with currently applied systems. Irrespective of whether it is CRM, ERP, or SCM systems, enterprise software solutions are designed to address specific organisational objectives and processes.
The practical use of custom enterprise software involves automating various processes within a business enterprise, thereby minimising errors from human input and providing more accurate information on which key decisions can be made instantly. It helps companies succeed in the market by allowing them to respond to changes effectively and satisfy customers’ needs by optimising business processes.
Types of Enterprise Software and Their Applications
Enterprise software comes in various forms, each catering to distinct business needs:
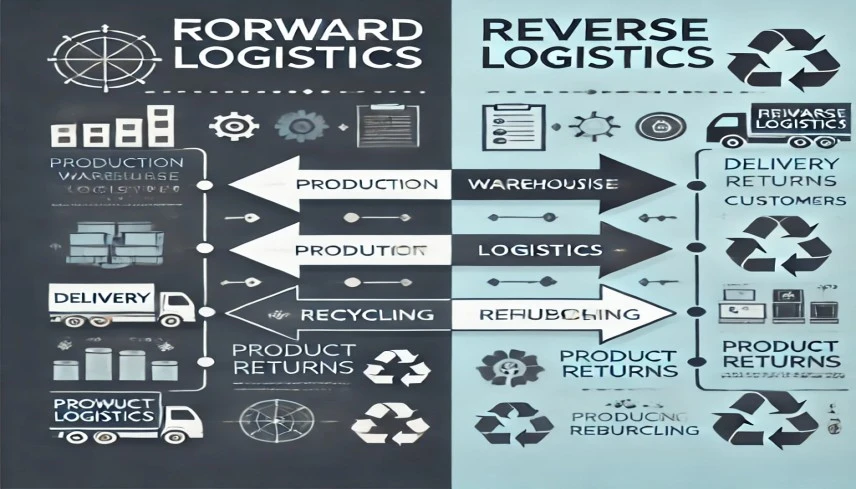
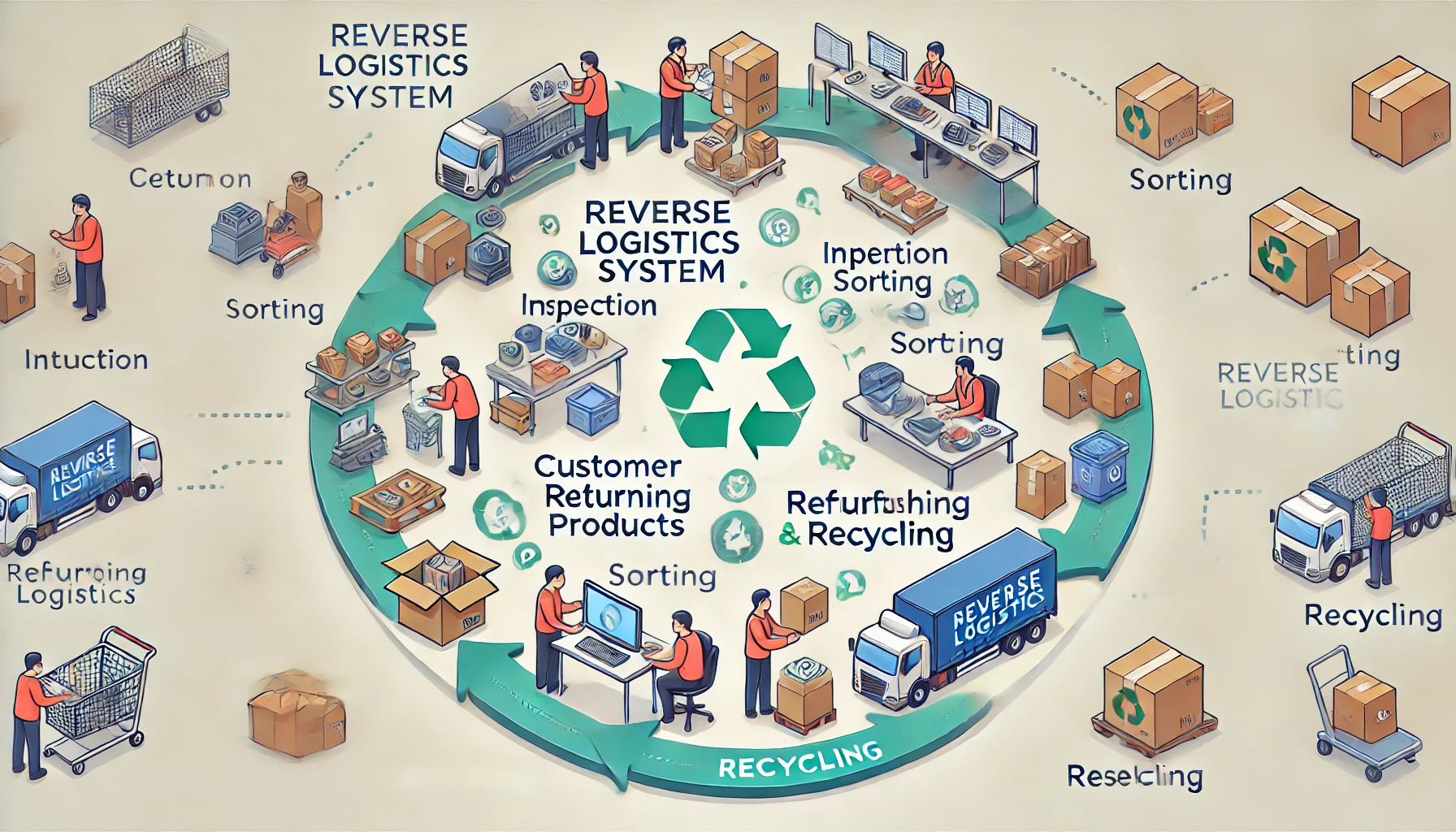
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP):
Connects essential business activities such as financial, human resources, and materials management into one system. - Customer Relationship Management (CRM):
Contributes to trending, selling, communication, and promotion processes. - Supply Chain Management (SCM):
Enables efficient supply chain management by managing supply chain, purchasing, and inventory flows. - Human Resource Management (HRM):
Illustrates the management of employees, compensation of employees, and the hiring of new employees.
The adoption of these systems therefore has the overall impact of enhancing coordination, communication, and efficiency between departments of an organisation.
Additional Key Aspects of Enterprise Software Development
- Customisability:
Enterprise software is designed to provide specific solutions to its users’ varied needs based on their functionality in organisations. - Interoperability:
Current enterprise software solutions must work in conjunction with other applications and systems that organisations already employ to transfer data or have functional interactions. - Scalability:
As the business expands, there must be a way for the software to handle more data, users, and functionalities than it currently supports. - Automation:
Processing routine and time-consuming assignments minimises human interference and time wastage while allowing employees to shift their time and effort towards the core goals of the organisation. - Real-Time Insights:
Enterprise software offers real-time data availability that allows organisations to make the best decisions. - User-Centric Design:
The interface of the system should be well-designed so that employees can embrace the use of the system with a reasonable sense of ease. - Compliance and Security:
Enterprise software aims at data security and follows the rules and regulations to prevent the leakage of valuable information. - Support for Mobile and Cloud Integration:
Contemporary enterprise applications extend functionalities for cloud and mobility, enabling employees to utilise tools and data on the move.
These aspects improve the value of enterprise software, proving its importance in enhancing the operations of businesses.
Strategic Benefits of Enterprise Software Development
Enterprise software development brings about the following benefits, positioning businesses for the long term. It helps to perform organisational operations more efficiently, increase resource use, and enhance inter-departmental collaboration. This means that most features can be altered to complement the company’s specific processes and goals.
Thus, enterprise software also helps organisations achieve their goals by becoming big data literate and making informed decisions based on such data. Thus, one of the approaches to reaching new heights is automating repetitive tasks or processes that slow the company down.
Conclusion
Implementing enterprise software is not merely a technological proposition; it is a business value-creation activity. Enterprise software plays an important role in various aspects, from improving operational capability to fostering innovation and growth in an increasingly challenging environment. Through the concept of solutions, organisations ensure that every system is optimised and that all its decision-making, from processes down to resources, mirrors its overall objectives. Therefore, as businesses continue to advance and sell their products and services, enterprise software will remain a useful tool in helping them achieve their vision of long-term success.